YOLT-203 Awarded EMA Orphan Drug Designation for Treatment of Primary Hyperoxaluria Type 1
CMN Intelligence - The World’s Most Comprehensive Intelligence Platform for CRISPR-Genomic Medicine and Gene-Editing Clinical Development
Providing market intelligence, data infrastructure, analytics, and reporting services for the global gene-editing sector. Read more...
Yoltech Therapeutics announced in a press release published on Monday that its investigational CRISPR therapy for primary hyperoxaluria type 1 (PH1), YOLT-203, has received Orphan Drug Designation from the European Medicines Agency. This designation follows Orphan Drug Designation and Rare Pediatric Disease Designation previously granted by the FDA in 2024.
YOLT-203 targets the HAO1 gene for permanent reduction of liver oxalate levels
PH1 belongs to a family of inherited metabolic disorders and arises through mutations in the AGXT gene, which results in deficiency or dysfunction of the enzyme alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase. This leads to harmful accumulation of oxalate in the kidney and other organs. PH1 typically debuts in childhood, and most patients experience kidney failure and require intensive haemodialysis while waiting for dual liver/kidney transplantation.
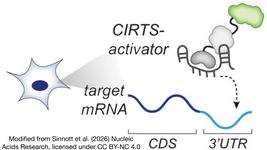
YOLT-203 is designed to permanently reduce the harmful oxalate levels in the blood by deactivating glycolate oxidase (GO), an enzyme encoded by the HAO1 gene and which plays a key role in oxalate production. By targeting HAO1 instead of AGXT, YOLT-203 has the potential to treat more patients, since PH1 can arise through many different mutations in AGXT.
YOLT-203 is developed using YolTech's proprietary YolCas12™ system and consists of the YolCas12 nuclease and target-specific guide RNA. This cargo is delivered intravenously via lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) that traffic to the liver, where it targets HAO1 in liver cells.
Clinical data shared in February 2025 from an early Phase 1 trial of YOLT-203 shows promising results for treating PH1. That trial, which is sponsored by RenJi Hospital in Shanghai, aims to evaluate the safety and tolerability of YOLT-203 in Chinese individuals with PH1, and to preliminarily assess the impact of a single dose of YOLT-203 on plasma oxalate levels. According to the company's press release and as summarised in a previous CMN clinical trial update, that data demonstrated excellent safety and pharmacodynamic profiles and the potential of YOLT-203 to effectively normalise urinary oxalate levels in PH1 patients. A smaller study (NCT06892301) sponsored by Guangzhou Women and Children's Medical Center has completed enrolment with 2 participants.
In February 2025, the FDA granted Orphan Drug and Rare Pediatric Disease designations to Arbor Biotechnologies' ABO-101, a one-time in vivo CRISPR-Cas12i2 therapeutic candidate for PH1 that is also delivered by LNPs to target HAO1. The Phase 1/2 redePHine trial of ABO-101, which is currently recruiting up to 23 participants, will evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and preliminary efficacy of ABO-101 in adult and paediatric PH1 patients (6 to 64 years old). You can read more about ABO-101 here.
We will continue to provide updates on YOLT-203 and other clinical trials for PH1 as new details emerge.
You can find all our previous news articles about gene-editing clinical trials here. For a complete overview of CRISPR IND approvals and ongoing gene-editing trials, check out CRISPR Medicine News' Clinical Trials Database.
To get more CRISPR Medicine News delivered to your inbox, sign up to the free weekly CMN Newsletter here.
Tags
ArticleNewsClinical News UpdatesPrimary hyperoxaluria (PH)YolTech Therapeutics
CLINICAL TRIALS
Sponsors:
Base Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Sponsors:
Base Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.