CelFi Assay Tracks Indels to Validate CRISPR Knockout Screens
CMN Intelligence - The World’s Most Comprehensive Intelligence Platform for CRISPR-Genomic Medicine and Gene-Editing Clinical Development
Providing market intelligence, data infrastructure, analytics, and reporting services for the global gene-editing sector. Read more...
“The CelFi assay offers a quick and reliable validation of fitness defects and is designed to complement follow-up efforts for identified hits from pooled CRISPR KO screens”Loughran et al.
A new study by researchers from St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, introduces the CelFi assay, which evaluates the functional impact of gene knockouts on cell proliferation by analysing the persistence of out-of-frame (OoF) indels in edited cell populations.
The method was validated across multiple genes and cell lines, revealing concordance with dependency scores from the Cancer Dependency Map (DepMap) and successfully identifying both false positives and negatives from CRISPR screens.
"The CelFi assay offers a quick and reliable validation of fitness defects and is designed to complement follow-up efforts for identified hits from pooled CRISPR KO screens," senior author Shondra Pruett-Miller and his colleagues state in the manuscript.
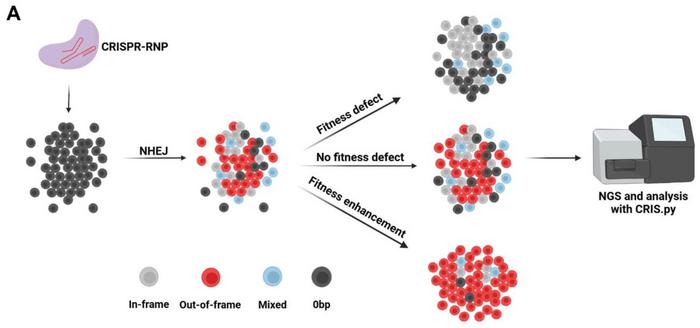
CelFi is implemented by transiently transfecting cells with Cas9-sgRNA ribonucleoproteins and tracking editing outcomes at the target locus via targeted deep sequencing at several time points (see Figure 1A). A reduction in OoF indels over time signals a fitness cost of gene disruption.
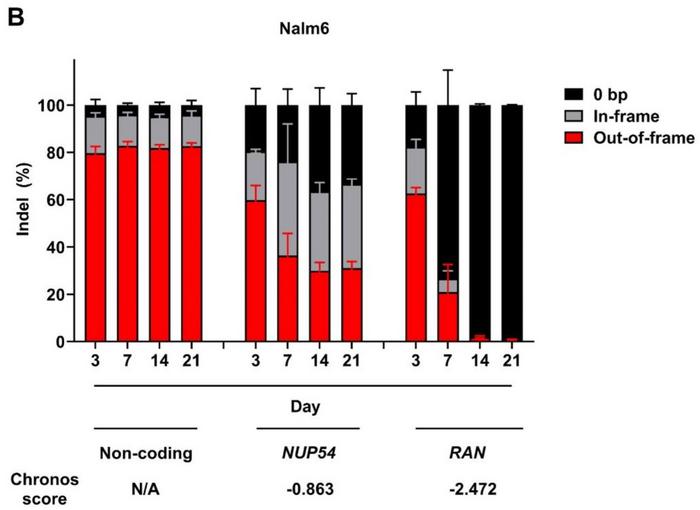
The authors validated the method by targeting known essential genes (e.g. RAN, NUP54) in Nalm6 cells, demonstrating a strong correlation between CelFi readouts and Chronos dependency scores (see Figure 1B).
Additionally, the assay identified false-negative hits such as SLC25A19, which exhibited fitness defects that were not detected in the original pooled screens. It also uncovered false positives like OTOP1, where gene knockout had little impact on fitness despite low Chronos scores.
"We were surprised to easily detect a false-positive hit. This further underlines the necessity of follow-up hit validation following a pooled screen," the authors highlight.
The assay was robust to variables such as sgRNA activity and gene copy number and adaptable to different cell lines and delivery formats. Furthermore, CelFi proved effective under drug treatment conditions, as shown with EIF2AK1 and dihydroartemisinin in B-ALL cells, indicating the potential for use in mechanism-of-action studies.
The authors recommend using multiple sgRNAs per gene and sequencing pooled, barcoded amplicons to reduce cost and maximise throughput.
This study was led by Allister Loughran and Shondra Pruett-Miller at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, USA. It was published in Scientific Reports on 17 April 2025.
To get more CRISPR Medicine News delivered to your inbox, sign up to the free weekly CMN Newsletter here.
Tags
CLINICAL TRIALS
Sponsors:
Base Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Sponsors:
Base Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.