CRISPR exposes ageing and mitotic stress in GATA2 deficiency
CMN Intelligence - The World’s Most Comprehensive Intelligence Platform for CRISPR-Genomic Medicine and Gene-Editing Clinical Development
Providing market intelligence, data infrastructure, analytics, and reporting services for the global gene-editing sector. Read more...
To create these models, the team used CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complexes, which deliver the nuclease and guide RNA directly into cells to generate a targeted DNA cut. The cells were then immediately transduced with recombinant AAV6 donor templates carrying the GATA2 R398W mutation and an in-frame GFP reporter, enabling homology-directed repair to insert the variant at the cut site. In parallel, the researchers applied multiplex editing to introduce mutations in SETBP1 (D868N) and ASXL1 (G646fs), two established cooperating lesions in myeloid disease (see Figure 1).
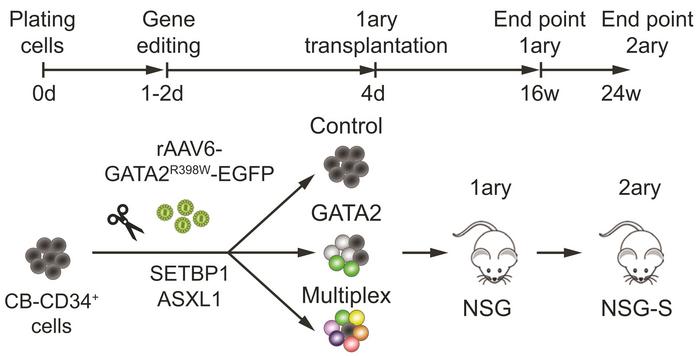
These edited haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells were then tested in competitive xenotransplantation assays in NSG/NSG-S mice to follow their clonal behaviour in vivo. In these experiments, GATA2-mutant clones gradually contracted, whereas clones carrying SETBP1 or ASXL1 mutations expanded. The findings indicate that GATA2 haploinsufficiency intrinsically reduces stem cell fitness even when other oncogenic mutations are present.
In vitro, R398W⁺ cells showed early proliferation failure, loss of CD34⁺ fraction, reduced G2/S/M, and a two-fold rise in mitotic errors (bridges, lagging chromosomes, multipolar spindles, misalignment). RNA-seq and ATAC-seq revealed downregulation of HSC self-renewal programmes, decreased TERT and regulators (with shorter telomeres by FISH), upregulation of CDKN2A/B/D and p53-linked stress, and a shift towards MEP priming. Allele-specific analysis showed overexpression of the mutant GATA2 allele.
Together, the data depict mitotic dysfunction and premature ageing as proximate mechanisms of stem/progenitor attrition, and suggest that partial correction of GATA2 could confer a selective advantage in vivo.
The study was led by Damia Romero-Moya, Alessandra Giorgetti, and colleagues from IDIBELL in Barcelona, as well as other Spanish institutions. It was published today in Leukemia.
To get more CRISPR Medicine News delivered to your inbox, sign up to the free weekly CMN Newsletter here.
Tags
ArticleCMN BriefsNewsRibonucleoprotein (RNP)Blood DiseaseHomology-directed Repair (HDR)Cas9
CLINICAL TRIALS
Sponsors:
Base Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Sponsors:
Base Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.