CRISPR PD-1 knockout allogeneic CAR-T matches autologous
CMN Intelligence - The World’s Most Comprehensive Intelligence Platform for CRISPR-Genomic Medicine and Gene-Editing Clinical Development
Providing market intelligence, data infrastructure, analytics, and reporting services for the global gene-editing sector. Read more...
“[With vispa-cel,] allogeneic CAR-T cell therapy can be on par with the efficacy and durability of autologous treatments”Rachel Haurwitz, Caribou Biosciences
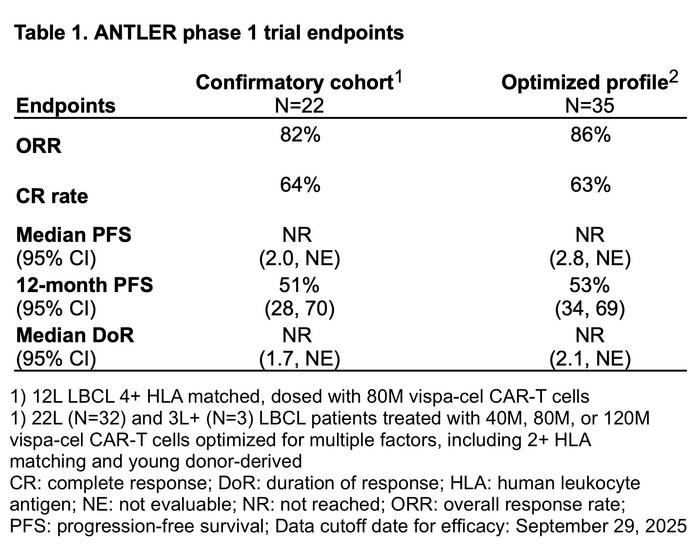
The ANTLER Phase 1 clinical trial evaluated vispacabtagene regedleucel (vispa-cel, formerly CB-010) in 84 patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, with particular focus on a 22-patient confirmatory cohort of second-line large B-cell lymphoma patients who had not previously received CD19-targeted therapy.
These patients received vispa-cel at the recommended Phase 2 dose of 80 × 106 CAR-T cells, following lymphodepletion with cyclophosphamide and fludarabine. The therapy achieved an 82% overall response rate, a 64% complete response rate, and 51% progression-free survival at 12 months – outcomes that match those seen with approved autologous CAR-T therapies in similar patient populations (see Table 1).
Vispa-cel is an allogeneic CAR-T product with enhanced activity against B-cell malignancies. It represents the first allogeneic CAR-T therapy in clinical testing to incorporate a PD-1 gene knockout, a modification designed to prevent premature T cell exhaustion and thereby sustain anti-tumour activity. The therapy uses T cells from healthy donors that are engineered to express an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor inserted into the TRAC locus while simultaneously disrupting the PD-1 gene through targeted genome editing.
PD-1 signalling hastens T-cell functional decline under chronic antigen exposure, and CRISPR disruption of PDCD1 in human CAR-T cells improves tumour control in xenografts. Multiple groups have shown that PD-1-deleted CAR-T cells resist PD-L1-mediated inhibition and clear tumours more effectively in vivo – evidence that a cell-intrinsic edit can substitute, at least transiently, for systemic checkpoint blockade.
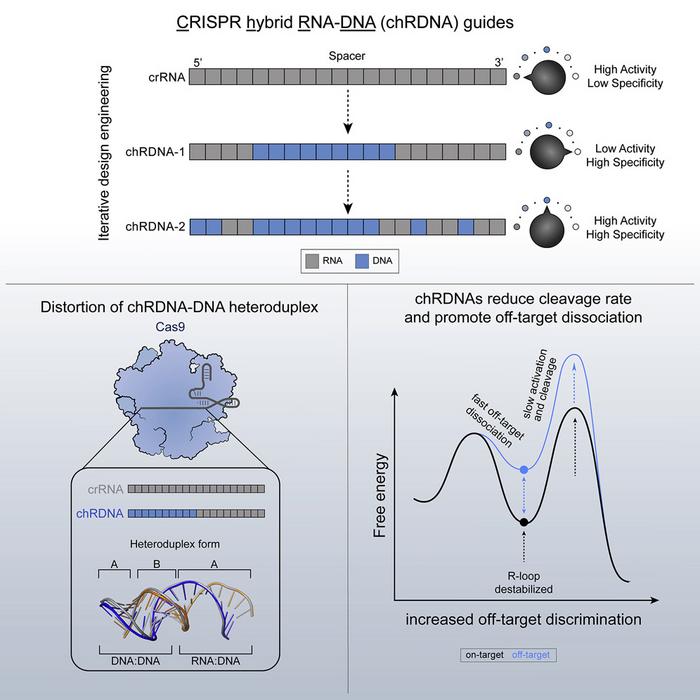
The therapy relies on the firm's Cas9 chRDNA (CRISPR hybrid RNA–DNA) gene-editing technology that replaces selected ribonucleotides within the guide with deoxynucleotides (see Figure 1). This approach weakens mismatched base-pairing, shifting the energy landscape against off-target duplex formation while preserving on-target cutting. Structural and cell-based work in primary T cells shows that such chRDNA guides can allosterically bias Cas9 into conformations that reduce off-target activity without sacrificing efficiency.
Following discussions with the US Food and Drug Administration, the regulatory pathway forward involves a randomised, controlled Phase 3 trial in approximately 250 second-line patients with large B-cell lymphoma who are CD19-naive and ineligible for transplant or autologous CAR-T therapy.
»We believe that with these results, Caribou has achieved what the field has long sought – strong evidence that an allogeneic CAR-T cell therapy can be on par with the efficacy and durability of autologous treatments and broaden access with a safety profile that allows for outpatient use,« said Rachel Haurwitz, president and chief executive officer of Caribou Biosciences, in a press release.
Patients randomised to the investigational arm would receive a single dose of vispa-cel containing 80 × 106 CAR-T cells. In contrast, those in the comparator arm would receive standard immunochemotherapy regimens selected by the investigators. The primary endpoint is progression-free survival, with an interim analysis planned. Secondary endpoints include overall response rate, complete response rate, duration of response, overall survival, quality of life, and safety.
The FDA has granted vispa-cel Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy designation, Orphan Drug designation, and Fast Track designation for B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Caribou Biosciences announced the ANTLER trial data on 3 November 2025.
To get more CRISPR Medicine News delivered to your inbox, sign up to the free weekly CMN Newsletter here.
Tags
ArticleNewsClinical News UpdatesIn vivoB-cell Malignancy, NHLNon-Hodgkin Lymphoma, NHLCancerCas9Caribou Biosciences, Inc.TrialsClinical
CLINICAL TRIALS
Sponsors:
Base Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Sponsors:
Base Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.