In Vivo T-Cell Editing in Lymph Nodes Effectively Combats Tumours
Researchers at City University of Hong Kong developed the technique that creates T-cells lacking PD1, a key immune regulator. The intervention improves their efficacy against tumour growth, metastasis, and recurrence in mice models.
Central to the new technique is a hydrogel-based electroporation system (hydro-EP) integrated into a surgical forceps-like device that delivers CRISPR-Cas9 plasmids targeting the PD1 gene into lymph node T-cells. During a minor surgical procedure, the lymph node is located and gently sandwiched between the hydro-EP device’s electrodes, one of which contains the preloaded plasmid DNA (see Figure 1).
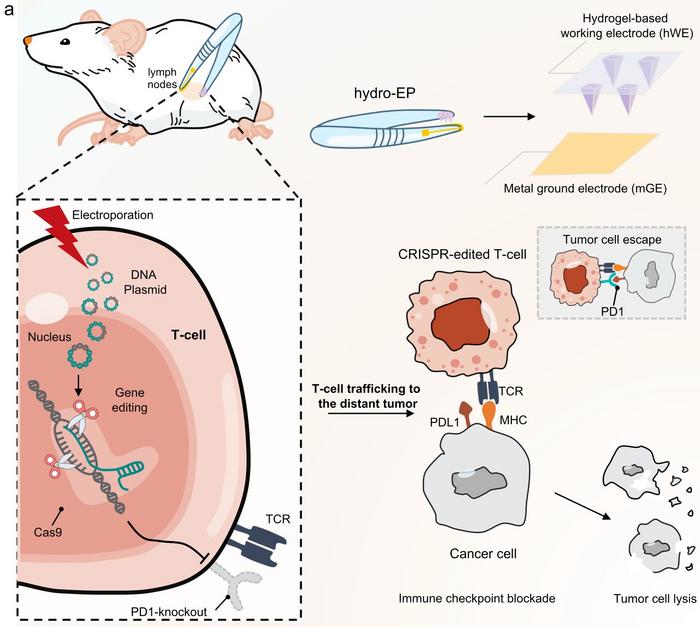
Mice treated with this method showed significant immune responses, with increased infiltration of effector T-cells into tumours, reduced metastasis, and prolonged survival. The edited T-cells showed sustained activity and eliminated tumour recurrence post-surgery in melanoma models.
The approach is presented as minimally invasive and scalable, reducing costs and risks associated with traditional methods like viral vectors. This proof-of-concept study suggests a potential for broader applications in treating cancers and complex diseases through localised gene editing.
The study was led by Peng Shi at City University of Hong Kong and published yesterday in Nature Communications.
To get more CRISPR Medicine News delivered to your inbox, sign up to the free weekly CMN Newsletter here.
Tags
CLINICAL TRIALS
Sponsors:
Suzhou Maximum Bio-tech Co., Ltd.
Sponsors:
Zhejiang University